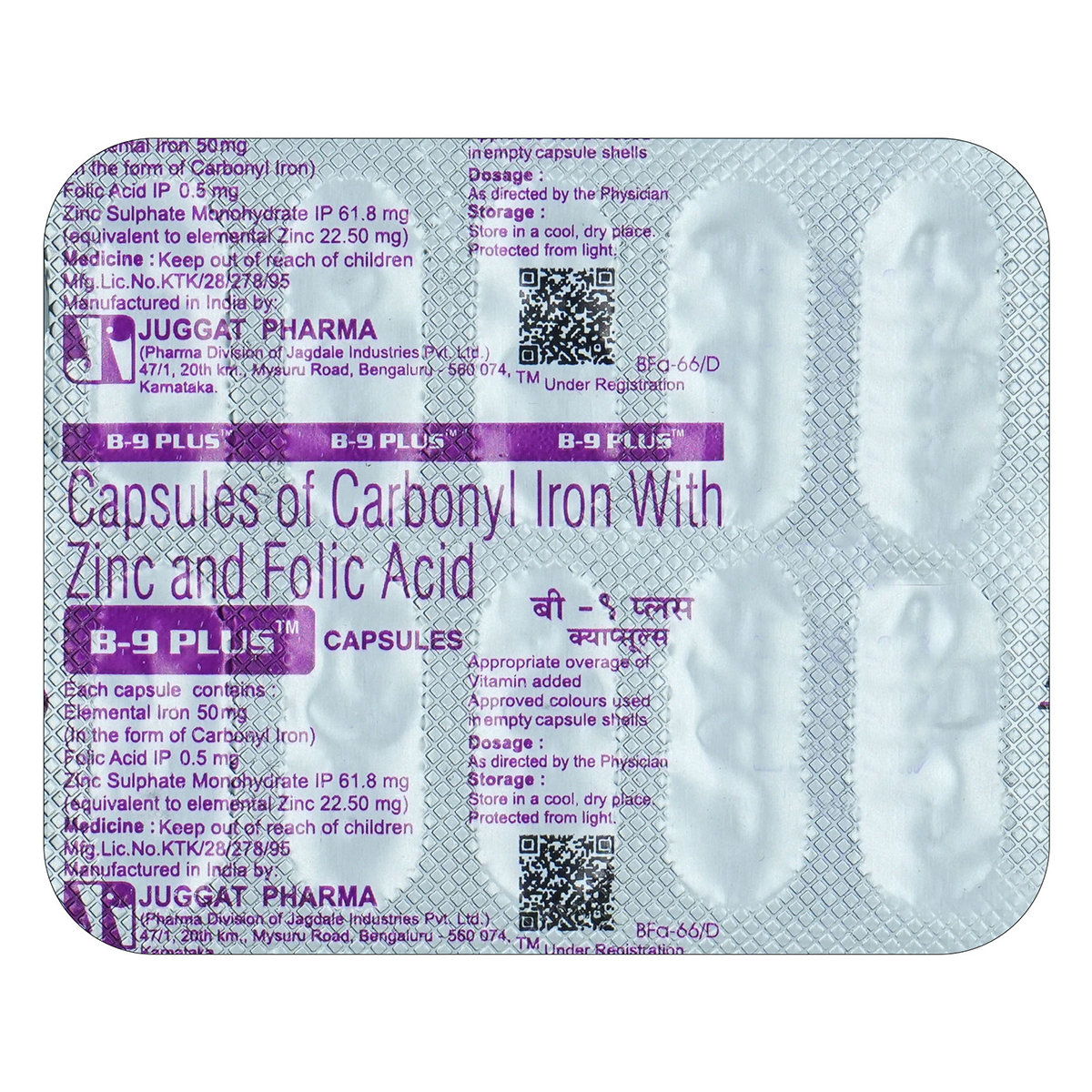
Zinc Sulfate+folic Acid
About Zinc Sulfate+folic Acid
Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate belongs to the class of 'dietary supplements', primarily used to treat nutritional deficiencies. Nutritional deficiency occurs when the body is unable to absorb or get enough nutrients from food.
Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate contains Zinc sulfate and Folic acid. Zinc sulfate is a mineral that promotes the growth and development of body tissues. It is essential for vision, fighting against rhinoviruses (that cause the common cold), immune function, bone metabolism, taste, wound healing, insulin production, blood clotting, and thyroid function. Folic acid, a form of Vitamin B, treats folic acid deficiency and anaemia (lack of red blood cells). It helps in the formation of red blood cells and prevents DNA changes that may lead to cancer.
Your doctor will decide the dosage based on your medical condition. Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate is likely safe to consume. Sometimes, it may have common side effects like abdominal pain, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and gastric irritation. These side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if these side effects persist longer, please consult your doctor.
If you are known to be allergic to Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate or its inactive components, please inform your doctor. Please tell your doctor if you have malabsorption syndrome (difficulty absorbing nutrition from food), cancer, coronary stent, seizures (fits), tumour, kidney dysfunction and undergoing dialysis. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate. Avoid consuming alcohol along with Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate to ensure maximum absorption of nutrients. Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate should be used in children only when the doctor has advised.
Uses of Zinc Sulfate+folic Acid
Medicinal Benefits
Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate contains Zinc sulfate and Folic acid. Zinc sulfate is a mineral that promotes the growth and development of body tissues. It is essential for vision, fighting against rhinoviruses (that cause the common cold), immune function, bone metabolism, taste, wound healing, insulin production, blood clotting, and thyroid function. It treats zinc deficiency, acute diarrhoea in children, slow wound healing, and Wilson's disease (a genetic disorder causing copper build-up in the body). Folic acid, a form of Vitamin B, is used to treat pernicious, aplastic, or normocytic anaemia (lack of red blood cells), low blood levels of folate (folate deficiency), and high blood levels of an amino acid, homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia). It helps in the formation of red blood cells and prevents DNA changes that may lead to cancer. Folic acid also prevents miscarriage and neural tube defects in infants when used by pregnant women.
Directions for Use
Storage
Side Effects of Zinc Sulfate+folic Acid
- Abdominal pain
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Gastric irritation
Drug Warnings
Please tell your doctor if you have allergic reactions to medicines, cancer, a coronary stent, seizures (fits), tumour, kidney dysfunction or undergoing dialysis before using Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate. Excessive alcohol consumption reduces absorption and increases the elimination of folic acid. Hence, please avoid alcohol while using the Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate. This supplement should be given to children only if a doctor has advised it. Keep Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate away from direct sunlight. Do not store Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate above 25ºC.
Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interaction: Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate may interact with blood clotting drugs, antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin), cancer medicines (cisplatin), arthritis drugs (penicillamine), water pills (amiloride), and medicines treating bone loss (alendronate).
Drug-Food Interaction: Excessive alcohol consumption reduces absorption and increases the elimination of folic acid. Hence, please avoid alcohol while using Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate.
Drug-Disease Interaction: Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate is to be used with medical advice if you have malabsorption syndrome (difficulty absorbing nutrition from food), cancer, coronary stent, seizures (fits), tumour, and kidney dysfunction.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List:
Safety Advice

Alcohol
cautionExcessive alcohol consumption reduces the absorption and increases the elimination of folic acid. Hence, please avoid alcohol while using Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate.

Pregnancy
cautionLet your doctor know if you are pregnant or planning to conceive before taking Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate.

Breast Feeding
cautionFolic Acid+zinc Sulfate may be excreted into the breast milk when used by a breastfeeding mother. Please consult your doctor before taking Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate if you are breastfeeding.

Driving
not applicableFolic Acid+zinc Sulfate usually does not interfere with your driving abilities.

Liver
cautionLet your doctor know if you have any history of liver diseases before taking Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate.

Kidney
cautionIt is advised to seek doctor advice before starting Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate if you have any kidney diseases. Your dosage may be adjusted, reduced, or omitted in case of renal dysfunction.

Children
consult your doctorThe doctor will decide the dosage of Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate based on the child's age and weight.
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Include zinc-rich sources like meat, shellfish, legumes, hemp seeds, nuts, eggs, dairy products, whole grains, potatoes, kale, and dark chocolate in your diet.
- Try folate-rich food sources like broccoli, brussels sprouts, leafy green vegetables, cabbage, kale, spring greens, spinach, peas, chickpeas, kidney beans, liver (avoid this during pregnancy), and breakfast cereals fortified with folic acid.
- Sprinkle sunflower seeds over your food, vegetables and salads.
- Please exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. It is better to avoid excess fatty foods.
Special Advise
- Clinical monitoring of zinc levels through blood examinations is recommended.
- Zinc sulfate in Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate may decrease the absorption of antibiotic, thereby reducing its effectiveness. It is advised to maintain at least an hour gap between Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate and other antibiotics.
Patients Concern
Disease/Condition Glossary
Nutritional deficiency: A nutritional deficiency occurs when the body does not absorb or get enough nutrients from food. This condition occurs when a person's nutrient intake is lesser than the body's recommended requirement. It can lead to various health problems like a weak immune system, skin problems, digestion problems, defective bone growth, and neurological diseases.
Zinc deficiency: When your body doesn't have adequate mineral levels called zinc, it leads to zinc deficiency. It causes hair loss, diarrhoea, delayed sexual maturation, impotence, hypogonadism (sex glands produce little or no sex hormones) in males, and eye and skin lesions.
Folate deficiency: Folate deficiency occurs when your body won't have enough folate in your diet. Symptoms include fatigue, grey hair, mouth sores, tongue swelling, and growth problems. Folate deficiency leads to anaemia.
Anaemia: It is a condition associated with a decrease in the red blood cells (RBCs) count or haemoglobin in the blood, or a lowered ability to carry oxygen. Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, light-headedness, dizziness and fast heartbeat.
FAQs
Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate is a dietary supplement and consists of Zinc sulfate and Folic acid. When you lack these minerals in your body, which cannot be recovered even with the food sources, Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate reduces these deficient levels. Collectively, Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate treats folate and zinc deficiencies, and anaemia.
Folate deficiency occurs when your body lacks adequate folic acid/folate levels. You can overcome this deficiency by including food sources rich in folic acid like broccoli, brussels sprouts, leafy green vegetables, cabbage, kale, spring greens, spinach, peas, chickpeas, kidney beans, liver (avoid this during pregnancy), and breakfast cereals fortified with folic acid. If your folic acid levels are still low, your doctor may suggest its supplements.
Zinc deficiency is caused when you don't have enough zinc levels in your body. You can include natural zinc sources like meat, shellfish, legumes, hemp seeds, nuts, eggs, dairy products, whole grains, potatoes, kale, and dark chocolate in your diet for treating zinc deficiency. If you still have low levels of zinc, please consult your doctor for zinc supplements.
Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate contains Zinc sulfate, which is primarily excreted in the urine. Hence, please let your doctor know if you have any kidney diseases since it may affect the excretion of Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate.
Zinc sulfate in Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate may decrease the absorption of antibiotic, thereby reducing the effectiveness of antibiotics. It is advised to maintain at least an hour gap between Folic Acid+zinc Sulfate and other antibiotics.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is time for the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and follow your usual dosage.